FD/Normalization exercize
Normalization results must be stated in relation schema format, identifying primary and foriegn keys where necessary.
- Given the relational schema R(A,B,C,D), A -----> B and B -----> C, determine which of the following dependencies are implied by the inference axioms. State the appropriate axioms if the dependency is implied.
- A -----> C Transitivity
- A -----> BC Transitivity (without b you can't have c)
- ACD -----> B Augmentation (you don't need C and D to get B)
- AC -----> C Augmentation (you don't need the C to get C)
- AD -----> BC Transitivity
- Inventory Control:
- A company wishes to create a database to control it's inventory, which consists of a number of products divided into a number of categories, such as clothing, food, and stationary. An employee raises a purchase order when a product has to be ordered from a supplier. The tracking records supplies recieved, units sold, and any wastage.
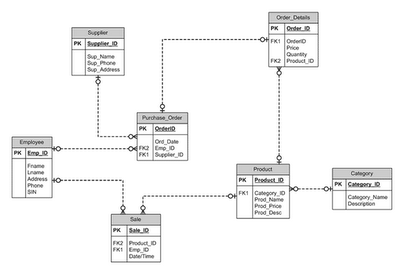
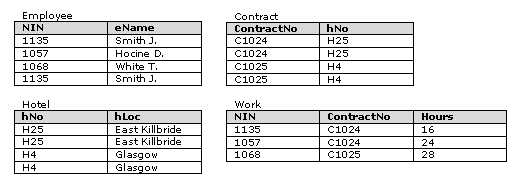
Draw the ERD for the inventory control system. - An agency called Instant Cover supplies part time/temporary staff to hotels within Scotland. The table below lists the time spent by agency staff working at various hotels. The National Insurance Number (NIN) is unique for each member of staff.
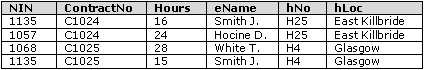
- This table is susceptible to update anomalies. Provide examples of insertion, deletion, and update anomalies.
insertion:- in order to add a contract you need an employee
- in order to add a new hotel you need an employee
- in deleting a contract info about an employee will be deleted
- in order to update a hotel location you must update every one in the table
info: grussel.org normalization article - Normalize this table to 3rd normal form. State any assumptions.