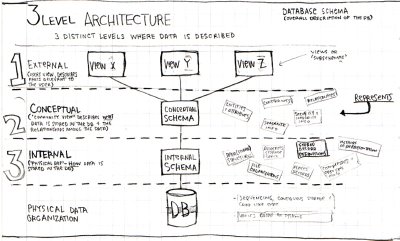
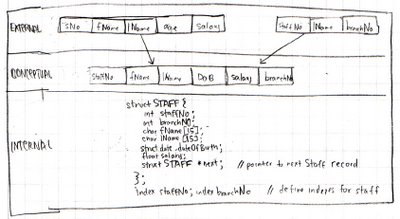
Definitions:
Relationships
--------------------------------------------------------------
Entity type: A group of objects with the same properties, which are identified by the enterprise as having an independent existence.
Entity Occurence: A uniquely identifiable object of and entity type.
Relationship Type: A set of meaningful associations among entity types.
Relationship Occurence: A uniquely identifiable association, which includes one occurence from each participating entity type.
Degree: (of a relationship) The number of participating entity types in a relationship.
Recursive relationship: A relationship type wher the same entity type participates more than once in
different roles.
Attributes------------------------------------------------------------------Attribute: A property of a relationship type.
Attribute domain: the set of allowable values for one or more attributes.
Simple attribute: An attribute composed of a single component with an independent existence.
Composite attribute: An attribute composed of multiple components, each with an independent existence.
Single valued attribute: An attribute that holds a single value for each occurence of an entity type.
Multi-valued attribute: An attribut that holds multiple values for each occurence of an entity type.
Derived attribute: An attribute that represents a value that is derivable from the value of a related attribute or set of attributes, not necessarily in the same entity type.
Keys-----------------------------------------------
Candidate key: The minimal set of attributes that uniquely identifies each occurence of an entitye type.
Primary key: The candidate key that is selected to uniquely identify each occurence of an entity type.
Composite key: A candidate key that consists of 2 or more attributes.
Entity Types
---------------------------------------------------
Strong Entity Type: An entity type that is
not existence-dependent on som other entity type.
Weak Entity Type: An entity type that is existence-dependent on some other entity type.
Structural Constraints
---------------------------------------------------
Multiplicity: The number (or range) of possible occurences of an entity ype that may relate to a single occurrence of an associated entity type thru a particular relationship.
Multiplicity (complex relationship): The number (or range) of possible occurrences of an entity type in an n-ary relationship when the other (n-1) values are fixed.
Cardinality: Describes the maximum number of possible relationship occurrences for an entity participating in a given relationship type.
Participation: Determines whether all or only some entity occurrences participate in a relationship.
ER Model Problematics
---------------------------------------------------
Fan Trap: Where a model represents a relationship between entity types, but the pathway between certain entity occurrences is ambiguous.